Rice farming is important for feeding millions of people. Success depends on using the right methods. A step-by-step process helps rice grow well and produce more. For instance, in Benin, rice production grew from 204,310 tons in 2015 to 406,000 tons in 2019. This happened because of better farming practices. Farmers who worked together or improved their soil grew more rice. By learning how to plant rice properly, you can grow more and help this important crop.
Plant Rice with Unmatched Accuracy Using the FJD AG1 Guidance System
Precision matters when planting rice, and the FJD AG1 Guidance System makes it simple. Designed for paddy field conditions, the AG1 system uses high-accuracy GNSS technology to guide tractors and rice transplanters along perfectly straight lines. This ensures uniform planting, maximizes field space, and improves irrigation efficiency. With easy-to-use controls and real-time positioning, farmers can achieve professional results in less time and with less effort.
Interested in improving your rice planting efficiency? Contact us for a quote today and bring precision farming to your fields!
Preparing for Rice Planting
Choosing High-Quality Rice Seeds
Picking good rice seeds is key to a great harvest. Quality seeds grow better, sprout evenly, and give more rice. Seeds with high germination rates grow fast and handle tough conditions well. Poor seeds grow unevenly and reduce the crop's success.

To find good rice seeds, check these things:
Germination Rate: Pick seeds with over 85% germination for steady growth.
Seed Purity: Make sure seeds are clean and free of pests or weeds.
Seed Size and Color: Same size and color often mean better quality.
You can test seeds at home by soaking some in water. After a few days, count how many sprout. This easy test shows if your seeds are ready for planting.
Testing and Preparing the Soil
Good soil is vital for growing healthy rice. Testing soil tells you its nutrients, pH, and condition. Rice grows best in rich soil with a pH of 5 to 7.5. Clay and silt soils hold water well, making them ideal.

A soil test gives useful details about your field. Check these:
Soil Test Parameter | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
pH | Impacts nutrients and soil health. |
Electrical Conductivity (EC) | Shows salt levels that may harm plants. |
Extractable Phosphorus, Potassium, etc. | Tells how much key nutrients are available. |
Nitrate-Nitrogen and Ammonium-Nitrogen | Measures nitrogen forms plants can use. |
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) | Shows soil's ability to hold nutrients. |
Organic Matter % | Helps soil keep water and nutrients. |
After testing, add compost or fertilizer to fix problems. Clear the field, plow it, and level it. This gets the soil ready for planting strong rice seeds.
Setting Up the Field for Wet or Dry Planting
Your planting method—wet or dry—depends on your area and tools. Wet planting floods the field, while dry planting uses less water and depends on rain or irrigation.
For wet planting, level the field and build bunds (raised edges) to hold water. This method controls weeds and keeps water steady. Studies show wet fields, like those with jute fabric, stay cooler and help seedlings grow better.

Dry planting needs soil that drains well. Plow the field to loosen the soil for roots. Remove debris and break big clumps. This method saves water but may need more weed control.
Both methods work well. Wet planting often grows more rice, while dry planting saves water. Pick the method that fits your field and resources.
How to Plant Rice
Getting Seeds Ready for Planting
Preparing seeds the right way helps them grow well. First, pick seeds that are pure and sprout easily. The strength of seeds depends on when they were harvested. Studies show harvesting seeds 17 to 23 days after pollination makes them better. This step is very important for good planting results.
Before planting, soak seeds in clean water for 1 to 2 days. This softens the outer layer and helps seeds sprout faster. After soaking, drain the water and leave the seeds in a warm, shady spot for another day. During this time, the seeds will start to sprout. Sprouted seeds grow roots quickly, giving your rice a strong start.
To check seed quality, try a simple water test. Put seeds in water and remove the ones that float. Floating seeds are often empty or damaged and won’t grow well. This quick test ensures you only plant the best seeds.
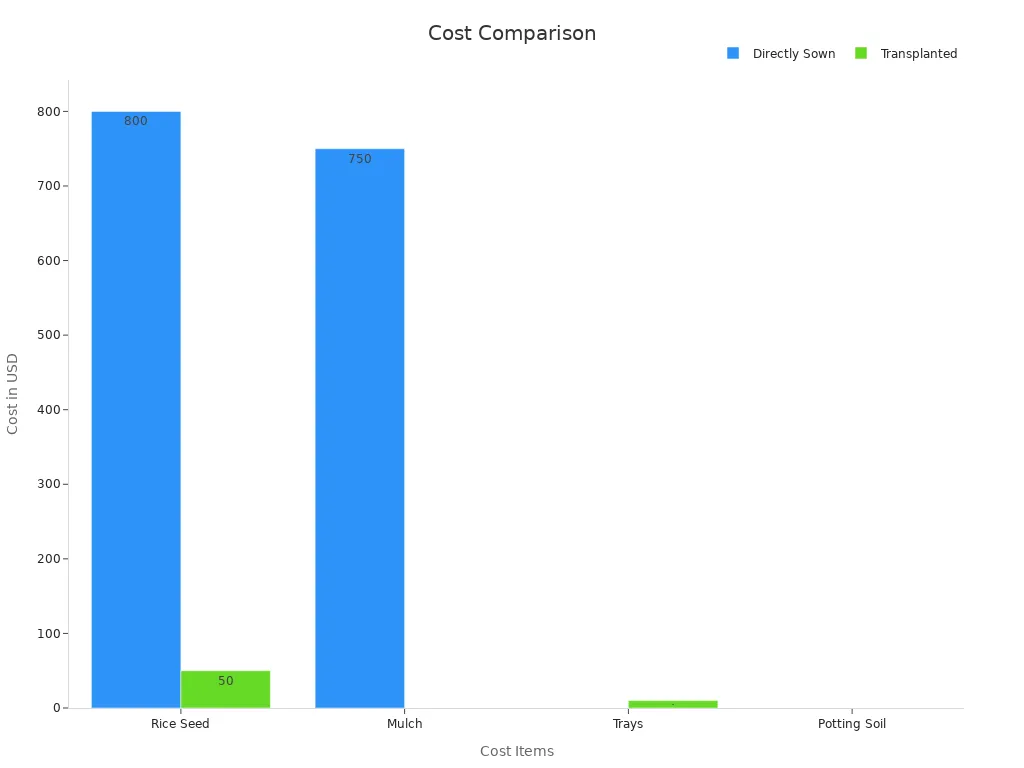
Direct Seeding vs. Transplanting
Choosing between direct seeding and transplanting depends on your tools and time. Each method has pros and cons. The table below shows the main differences:
Aspect | Direct Seeding (DSR) | Transplanting (PTR) | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
Yield Improvement | Small increase | Normal | - |
Extra Income | ₹5192/acre | Normal | +₹5192/acre |
Irrigation Cost | Lower | Higher | - |
Land Prep Cost | Lower | Higher | - |
Fertilizer Cost | Lower | Higher | - |
Direct seeding means planting seeds straight into the field. It saves time and effort since you skip moving seedlings. It also uses less water and costs less to prepare the land. But, direct seeding might give slightly lower yields than transplanting.
Transplanting involves growing seedlings in a nursery first. Then, you move them to the field. This method needs more work and water but often grows more rice. Transplanted rice usually has stronger roots, which helps plants grow better.
Research shows direct seeding costs less but produces about 9% less rice than transplanting. Transplanting costs almost twice as much in labor and supplies. Think about your budget and tools before choosing a method.
Best Spacing and Depth for Planting
Spacing and depth are key to growing more rice. Proper spacing gives each plant enough sunlight, water, and nutrients. For most rice types, 25×25 cm spacing works best. This distance helps plants grow more grains and stay healthy. It also reduces competition between plants.
"Planting rice 25×25 cm apart improves yield and reduces costs. This spacing helps plants grow more grains and need fewer seeds and nutrients."
When planting, make sure seeds are at the right depth. For direct seeding, plant seeds 2 to 3 cm deep. This keeps seeds safe from pests and birds while helping them sprout. For transplanting, plant seedlings 3 to 4 cm deep. Don’t plant too deep, as it can slow root growth.
By following these steps, you can plant rice successfully and grow a healthy crop.
Caring for the Rice Crop
Managing Water and Irrigation
Water is very important for growing rice. Giving rice enough water helps it grow strong and produce more. Pick the best irrigation method to save water and keep plants healthy. Traditional flooding uses a lot of water but wastes much of it. New methods like alternate wetting and drying (AWD) save water and grow more rice. AWD can cut water use by 30%, making it a smart and eco-friendly choice.

In China, the Beitang irrigation system shows how good water management works. This old system uses small ponds to share water wisely. It helps both crops and nature. Using similar ideas can help you save water and grow better rice.
Here’s a table comparing water use for different methods:
Method | Water Use Efficiency | Water Savings | Yield Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
Traditional Flooding | Low | High | Lower Yield |
Alternate Wetting and Drying | Big Savings | Higher Yield | |
Drip Irrigation under Mulching | 1.45–1.56 kg·m−3 | Less Savings | Best Yield |
Check water levels often to adjust your watering plan. This way, plants get enough water without wasting it.
Fertilizing for Healthy Growth
Fertilizers help rice grow strong and give better harvests. Use a mix of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). At planting, use half the nitrogen and all the phosphorus and potassium. Add the rest of the nitrogen later in two parts during the season.
Adding gypsum improves soil and helps plants take in nutrients. Research shows 750 kg ha−1 of gypsum boosts rice growth by holding water and nutrients better. During the Kharif season, 450 kg ha−1 of sugar beet gypsum gave higher yields. Gypsum also helps plants absorb calcium, magnesium, and zinc for healthy growth.
Tip: Mix organic compost with chemical fertilizers. This makes the soil richer and reduces the need for chemicals.
Controlling Weeds, Pests, and Diseases
Weeds, pests, and diseases can hurt your rice crop. Check your field often to catch problems early. Remove weeds by hand or use herbicides. Keeping the field wet at the start also stops weeds from growing.
To fight pests, bring in natural helpers like spiders or frogs. They eat harmful bugs without using chemicals. If pests stay, use small amounts of pesticides carefully to protect good insects.
Diseases like rice blast and bacterial blight spread fast. Use disease-resistant seeds and plant with enough space between them. Good spacing improves airflow and lowers humidity, stopping fungus from growing.
By handling these issues, you can keep your rice healthy and have a great harvest.
Watching Growth and Changing Care
Watching your rice plants grow is very important. It helps you fix problems early and have a good harvest.
First, check if your plants have enough water. Smart watering methods like alternate wetting and drying (AWD) save water and keep plants healthy. Use tools like the Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) to check soil moisture. This shows when and how much water to give.
Adding fertilizer at the right time helps plants grow strong. Use the right amount to avoid wasting it. Tools like Variable Rate Application (VRA) spread fertilizer evenly. This way, all plants get the nutrients they need.
Weeds and pests can harm your rice. Weeds take water and nutrients from your plants. Pests can damage them too. Check your field often and pull out weeds by hand or use herbicides. Frogs and spiders eat pests naturally. If needed, use small amounts of pesticides to protect helpful insects.
Watch for diseases like rice blast or bacterial blight. Tools for spotting diseases early can help. Plant disease-resistant rice and leave space between plants. This improves airflow and keeps fungus away.
Tip: Write down what you see and do in a field journal. This helps you learn and improve your care plan.
By keeping an eye on your plants and making changes, your rice will grow well and stay healthy all season.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling
Knowing When to Harvest
It’s important to harvest rice at the right time. Watch your fields as the rice ripens. Harvest when 80-90% of the grains turn golden yellow. At this point, the grains are fully grown and have the most starch. Waiting too long can cause grains to fall off and lose quality.

Check the grain moisture level before harvesting. It should be between 20-24%. Use a moisture meter to check this accurately. Harvesting too early means grains won’t be fully grown. Harvesting too late can lead to pests and diseases harming the crop.
Best Ways to Harvest Rice
Using proper harvesting methods helps you get the best yield. For small farms, cut rice stalks by hand with a sickle or scythe. This takes more work but reduces grain loss. It’s a good choice for smaller fields.
For bigger fields, machines save time and effort. Mechanical harvesters cut, thresh, and clean the rice all at once. They lower labor costs and work faster. Adjust the machine settings to avoid damaging the grains.
After cutting, leave the stalks to dry in the field for one or two days. This step lowers the moisture level and gets the grains ready for threshing.
Storing and Processing Rice
Storing and processing rice properly keeps it safe and high-quality. First, dry the grains until the moisture is 12-14%. This stops mold from growing and makes storage easier. Use a clean surface or a mechanical dryer for drying.
Store the dried rice in airtight bags or containers. Keep it away from damp places to avoid pests and moisture. Poor storage can ruin up to 30% of the harvest. In some areas, like Tar Pat Village in Myanmar, losses have reached 50%. Drying and storing rice correctly can prevent these problems.
Processing removes the husk and polishes the grains. Modern rice mills do this efficiently and reduce broken grains. Following these steps helps keep your rice fresh and increases its value.
FAQ
What are the best ways to plant rice?
You can pick direct seeding or transplanting. Direct seeding means planting seeds straight into the field. Transplanting involves growing seedlings first, then moving them to the field. Both methods work, but transplanting often grows more rice. Choose the one that fits your tools and time.
What type of soil is best for rice?
Rice grows well in clay or silt soils that hold water. The soil's pH should be between 5 and 7.5. Testing the soil helps you know its condition and fix any problems for better growth.
How much water does rice need to grow?
Rice needs steady water, especially when it starts growing. Flooding uses a lot of water, but newer methods like alternate wetting and drying save water. These methods help rice grow well and waste less water.
What are the best conditions for growing rice?
Rice grows best in warm weather, between 70°F and 100°F. It needs lots of sunlight and water. Preparing the soil, watering, and adding fertilizer help create the best growing conditions.
How do you stop pests and diseases in rice fields?
Check your fields often to find problems early. Use frogs or spiders to eat harmful bugs. For diseases, plant resistant seeds and leave space between plants. If needed, use small amounts of pesticides to protect helpful insects.