Alternative agriculture employs methods that safeguard both nature and human health. These practices are instrumental in addressing significant challenges in 2025, such as climate change and food scarcity.
Farms that adopt alternative agriculture principles frequently produce 10-20% more crops. The food they yield can contain up to 25% more nutrients. By enhancing soil health, alternative agriculture contributes to the development of resilient food systems and improved environmental conditions.
Principles of Alternative Agriculture
Sustainability and Resource Conservation
By using sustainable farming, you help save the planet's resources. Alternative agriculture uses methods that protect nature and improve soil and water. For example, regenerative farming adds nutrients back to the soil. This reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. It also increases crop growth and lowers pollution.
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) says farming must meet today’s and future needs. Sustainable farming keeps the economy strong, the environment healthy, and people treated fairly. Studies in Zhejiang, China, show resource-saving methods help farmers earn more. These methods also give communities better access to healthy food.

Biodiversity and Ecological Balance
Biodiversity is key to keeping nature balanced. Alternative farming supports growing different crops to keep ecosystems healthy. For example, mineral-ecological cropping systems (MECS) grow 90% as much as regular farming. They also produce 1.8 times more than organic farming. MECS earn 37% more profit than traditional methods.
When you focus on biodiversity, you protect pollinators and reduce pests. It also improves soil and helps farms handle climate change better. Growing many crops and adding trees to farms creates a strong system. This system works well without needing many chemicals.

Community and Social Equity
Alternative farming builds stronger communities by being fair and inclusive. Community-supported agriculture (CSA) helps include everyone in farming decisions. These programs give people healthy food and let them help grow it.
Studies show urban farming improves food access and brings people together. CSA programs create strong friendships and lasting support. By working with your community, you build a helpful network for everyone.
Objective | Description |
|---|---|
Promote Inclusion | Urban farming improves food access and brings people together. |
FJD Hydraulic Autosteering Kit – Driving Precision in Alternative Agriculture
The FJD Hydraulic Autosteering Kit empowers farmers practicing alternative agriculture—such as organic, regenerative, or permaculture systems—with precision steering technology that minimizes input waste, protects fragile ecosystems, and supports soil-conscious farming methods.
Why It Matters in Alternative Agriculture
High-Precision Steering for Delicate Systems - Achieve ±2.5 cm accuracy even in low-till, strip-till, or no-till environments—ensuring every plant, row, and pass aligns with your sustainability goals.
Soil Health First - By maintaining straight lines and reducing compaction from overlapping passes, it helps protect soil structure and microbial activity—core values of regenerative agriculture.
Supports Diverse Crop Layouts - Works seamlessly across mixed-cropping, companion planting, and high-value specialty crops, ensuring consistent row spacing and efficient land use.
Whether you’re planting heritage grains, managing a market garden, or building a biointensive farm, the FJD Hydraulic Autosteering Kit helps you stay accurate, efficient, and aligned with the values of alternative agriculture.
👉 Learn More on the Product Page
Benefits of Alternative Agriculture
Environmental Advantages
Alternative agriculture helps the environment in many ways. Using sustainable methods can cut pollution, save water, and make soil healthier. For example, no-till farming and cover crops improve soil and hold more water. This means less irrigation is needed and soil stays in place.
A study compared organic and regular farming to show the benefits. Organic farming lowers greenhouse gases and improves soil. But it might need more land to grow the same food. Finding a balance is key to helping the environment.

Case Study Location | Practices Used | Economic Results |
|---|---|---|
California | Tried different alternative methods | |
Pennsylvania | Used sustainable farming methods | Higher profits reported |
Economic Opportunities
Alternative farming opens new ways to earn money for farmers. Methods like crop rotation and pest management (IPM) can boost crops and cut costs. IPM uses natural ways to fight pests, so fewer chemicals are needed. Crop rotation keeps soil healthy, which helps plants grow better.
Practice | Economic Impact | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Results depend on crop type and carbon source in ASD. | |
Cover Cropping | Healthier soil over time | Short-term profits may be low; subsidies can help adoption. |
Regenerative farming also helps with tough weather. No-till farming lets water soak into the ground, helping crops in dry times. Growing different crops in rotation boosts harvests, even in bad conditions.
Regenerative farming helps crops grow during tough weather.
Managing cover crops well saves money and works better.
Rotating crops leads to bigger harvests in hard times.
Social and Community Impact
Alternative farming builds stronger communities by being fair to everyone. Programs like community-supported agriculture (CSA) connect farmers and buyers. These programs give people fresh food and bring them closer together.

Studies show CSA farmers are happier than regular farmers. For example, Romanian CSA farmers feel more respected. In Spain, CSA farms make 50-75% more money than regular farms.
Study | Findings |
|---|---|
Hunter et al. (2022) | CSA farmers feel happier and hopeful about the future. |
Moellers and Bîrhală (2014) | Romanian CSA farmers feel valued and satisfied. |
Pérez-Neira and Grollmus-Venegas (2018) | Spanish CSA farms earn 50-75% more than regular farms. |
Zhen et al. (2020) | CSA farms make nearly three times more profit per hectare. |
Joining a CSA program helps create a fairer food system. These programs close pay gaps and give farmers better chances to succeed.
Challenges of Alternative Agriculture
Cost and Financial Barriers
Switching to alternative farming can be very expensive. Many farmers struggle because they don’t have enough money to start. For example:
Farmers often lack funds to try new farming methods.
Sustainable practices can cause income loss or extra costs without help.
Here’s a closer look at the financial issues:
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Net Farm Income | Expected to drop by nearly 40% since 2022. |
Decline in Number of Farms | Over 140,000 farms disappeared between 2017 and 2022. |
Rising Production Costs | Fodder prices in India rose over 30%, hurting profits. |
Stagnant Market Prices | Farmers can’t cover higher costs, making money problems worse. |
Farmers need financial help to keep their farms running. You can support policies for subsidies or loans to reduce these struggles.
Education and Awareness
Many farmers don’t know much about sustainable farming. They don’t understand the benefits or how to use these methods. A study of farmers in Tanzania found:
72% had no basic soil knowledge.
Only 24% asked experts for farming advice.
65% didn’t know about farming support groups.
These education gaps stop farmers from improving their practices. You can help by sharing knowledge through workshops and community programs. Teaching farmers gives them the tools to make better choices and try sustainable farming.
Scalability and Market Access
Growing alternative farming to feed the world is hard. Small farmers face high transport costs and feel cut off from markets.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Market Access Challenges | Small farmers pay high transport costs and feel isolated from markets. |
Impact of Infrastructure | Better roads boost local economies and farm incomes. |
Importance of Technology | Credit and storage tools stabilize food prices and help profits grow. |
Improved roads and storage can lower costs and help farmers earn more. Supporting these changes builds a fairer and stronger food system.

Future Outlook: Why Alternative Agriculture Matters in 2025
Trends in Sustainable Farming Practices
Sustainable farming is growing fast as farmers protect nature. Blockchain helps track food better and grows 45% yearly. Big food companies are investing in this technology. AI tools help farmers plan smarter, boosting crops by 20-30%.
Saving water is also a big focus. Better irrigation systems cut water waste by half. Organic food is becoming very popular. By 2030, it may be worth $620 billion. This shows people want food that is natural and eco-friendly.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Blockchain adoption | Growing at 45% yearly, helps track food better. |
AI-driven climate models | Boost crop growth by 20-30%. |
Water waste reduction | Better irrigation cuts water waste by 50%. |
Organic food market | Could reach $620 billion by 2030. |
Innovations in Technology and Methods
New technology is changing farming. Precision farming uses data to grow crops better. It could grow from $9.8 billion in 2022 to $34.01 billion by 2032. Biotechnology is also growing fast. By 2032, it may be worth $242.17 billion.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is helping farms too. Sensors check soil and weather to guide farmers. These tools save resources and grow more food.
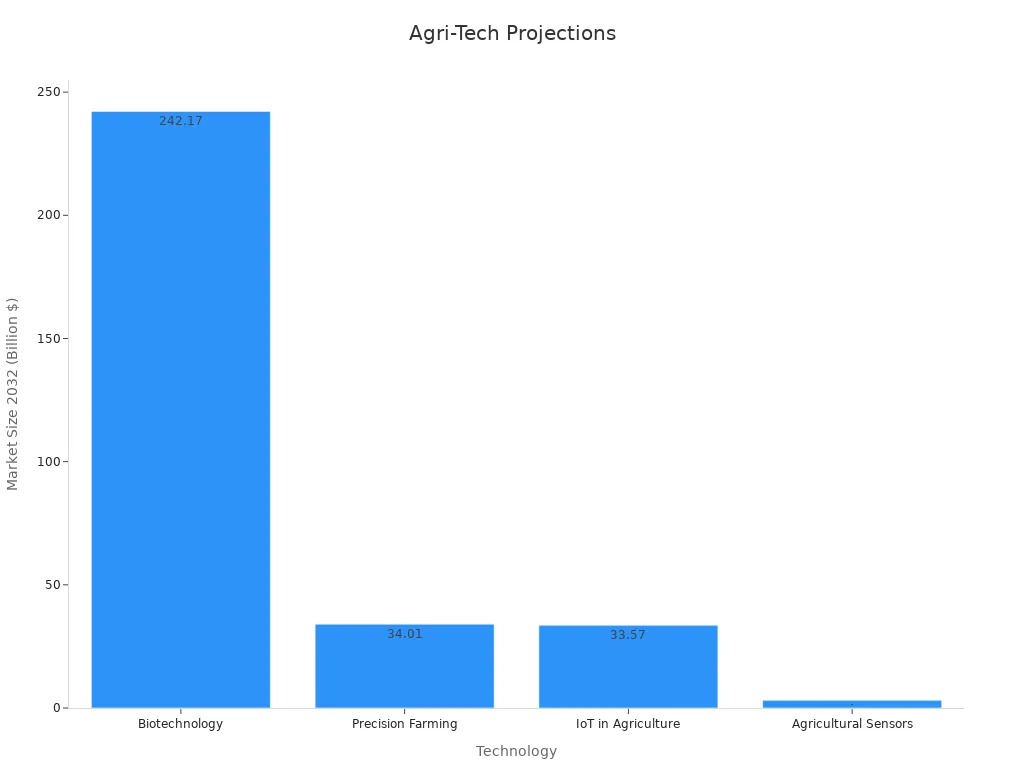
Technology | Market Size (2022) | Projected Market Size (2032) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
Biotechnology | $106.62 billion | $242.17 billion | N/A |
Precision Farming | $9.8 billion | $34.01 billion | 13.30% |
IoT in Agriculture | $13.61 billion | $33.57 billion | 9.5% |
Agricultural Sensors | N/A | $3.1 billion | N/A |
Role in Addressing Global Food Security
Alternative farming helps solve food problems worldwide. It builds strong food systems that handle climate change. Governments need to make rules and give support for sustainable farming.
Progress can be tracked with tools like the Countdown. It checks 50 things to improve food systems. These tools help leaders focus on what matters most. Supporting alternative farming creates a fairer and greener food system.
The Countdown tracks 50 key areas in food systems.
Strong food systems need both resilience and efficiency.
Governments can help with rules and support for farmers.
FAQ
What makes alternative agriculture different from regular farming?
Alternative farming cares about nature, variety, and people’s well-being. Regular farming often focuses on growing lots of food quickly. This can harm the environment. Alternative farming tries to grow food while keeping nature healthy.
How can you start using alternative farming methods?
Start small with crop rotation or composting. These steps make soil better and use fewer chemicals. You can also join local workshops to learn more ways to farm sustainably.
Can small farms use alternative farming?
Yes, small farms can use these methods easily. Ideas like pest control and urban farming help small farms grow more. Joining local markets or CSA programs can also help small farms earn more money.
Is alternative farming more expensive than regular farming?
It can cost more at first because of new tools. But over time, you save money with healthier soil and fewer chemicals. Grants and subsidies can help with starting costs.
How does alternative farming help the planet?
Alternative farming cuts pollution and makes soil healthier. It uses fewer chemicals and stores carbon in the ground. These methods help farms handle bad weather and protect the Earth.